Understanding EV Charging Connectors
The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) is changing the landscape of the automotive industry, with more people opting for eco-friendly, energy-efficient alternatives to traditional gasoline-powered cars. One of the critical components of this transition is the EV charging infrastructure, which includes various charging connectors to accommodate different types of EVs and charging stations. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of EV charging connectors, explore the key types, and understand their geographic usage.
What is an EV Charging Connector?
An EV charging connector links your electric vehicle and the charging station or power source. It allows electricity to flow from the source to your vehicle’s battery, replenishing energy reserves. These connectors come in various types and standards to cater to different charging requirements and vehicle models.
Main Types of EV Charging Connectors
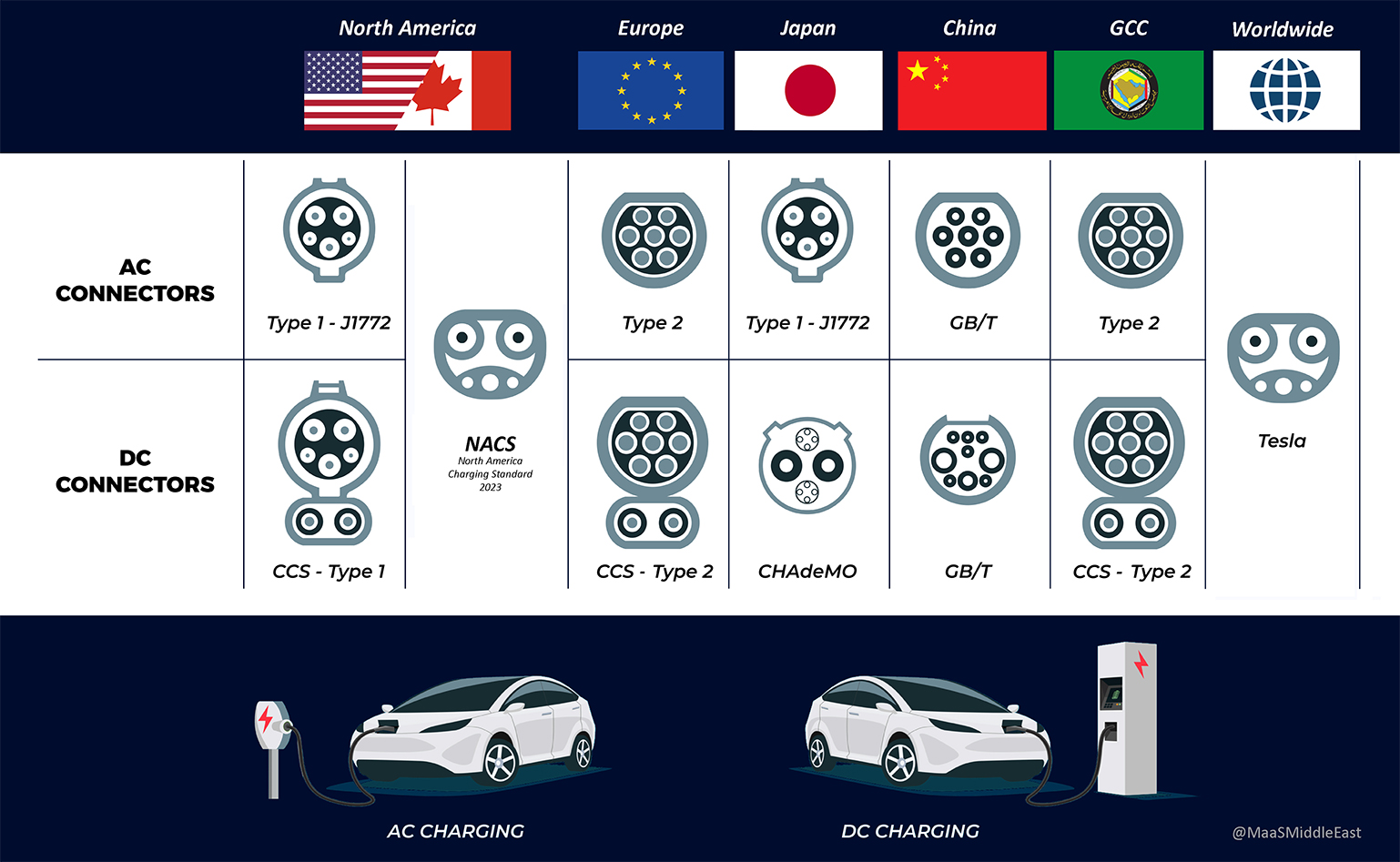
- Type 1 Connector
Type: AC Connector
Geographic Usage: North America, Japan
Type 1 connector, also known as J1772, is a standard AC connector primarily used in North America and Japan. It’s designed for Level 1 (120V) and Level 2 (240V) charging, making it suitable for residential and workplace charging. This connector is known for its safety features and widespread availability across the United States, Canada, and Japan. - Type 2 Connector
Type: AC Connector (Level 2)
Geographic Usage: Europe, Middle East
Type 2 connector, also known as the Mennekes connector, is a prevalent AC connector in Europe and GCC. It’s suitable for Level 2 (240V) charging and is widely adopted across the European continent, providing compatibility for various EV models. Type 2 Connector is the most commonly used EV charging connector in Dubai and many other cities across the Middle East. - CCS (Combined Charging System)
Type: DC Connector (Fast Charging)
Geographic Usage: Europe, North America, Middle East, and Growing Worldwide
The Combined Charging System (CCS) connector is gaining popularity worldwide for its versatility. It combines the capabilities of a DC connector for fast charging. The CCS concept is used for both Type 1 & Type 2 Connectors. CCS is becoming the standard in Europe and is gradually expanding to other parts of the world, making it a future-proof choice for many EV owners. - CHAdeMO Connector
Type: DC Connector (Fast Charging)
Geographic Usage: Japan, Some Other Regions
CHAdeMO is a DC fast charging connector developed in Japan. It is renowned for its high charging power, making it an excellent choice for electric vehicles with larger batteries. While it’s commonly used in Japan, you can also find CHAdeMO connectors in other regions, particularly in Asia and parts of Europe. - GB/T (Guobiao) Connector
Type: Hybrid Connector (AC and DC)
Geographic Usage: China
GB/T Connector
China has its own EV charging connector standard called GB/T. This connector serves both AC and DC charging needs within the country. As China continues to lead in the electric vehicle market, the GB/T connector remains a vital component of its charging infrastructure. - Tesla Supercharger Connector/ NACS
Type: Proprietary DC Connector
Geographic Usage: North America, Tesla Supercharger Network Worldwide
SAE International recently announced that it will standardise the Tesla-developed connector to become the North American Charging Standard (NACS). This standard (Also known as SAE J3400) has garnered support from several major automakers including Ford, General Motors, Honda, Mercedes-Benz, Nissan, Polestar, Rivian, and Fisker. Additionally, there is growing interest from other companies such as Stelantis, Hyundai, and Lucid, who are contemplating joining this standardization effort.
What is the difference between AC vs DC Chargers?
Here are some key distinctions between AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current) chargers:
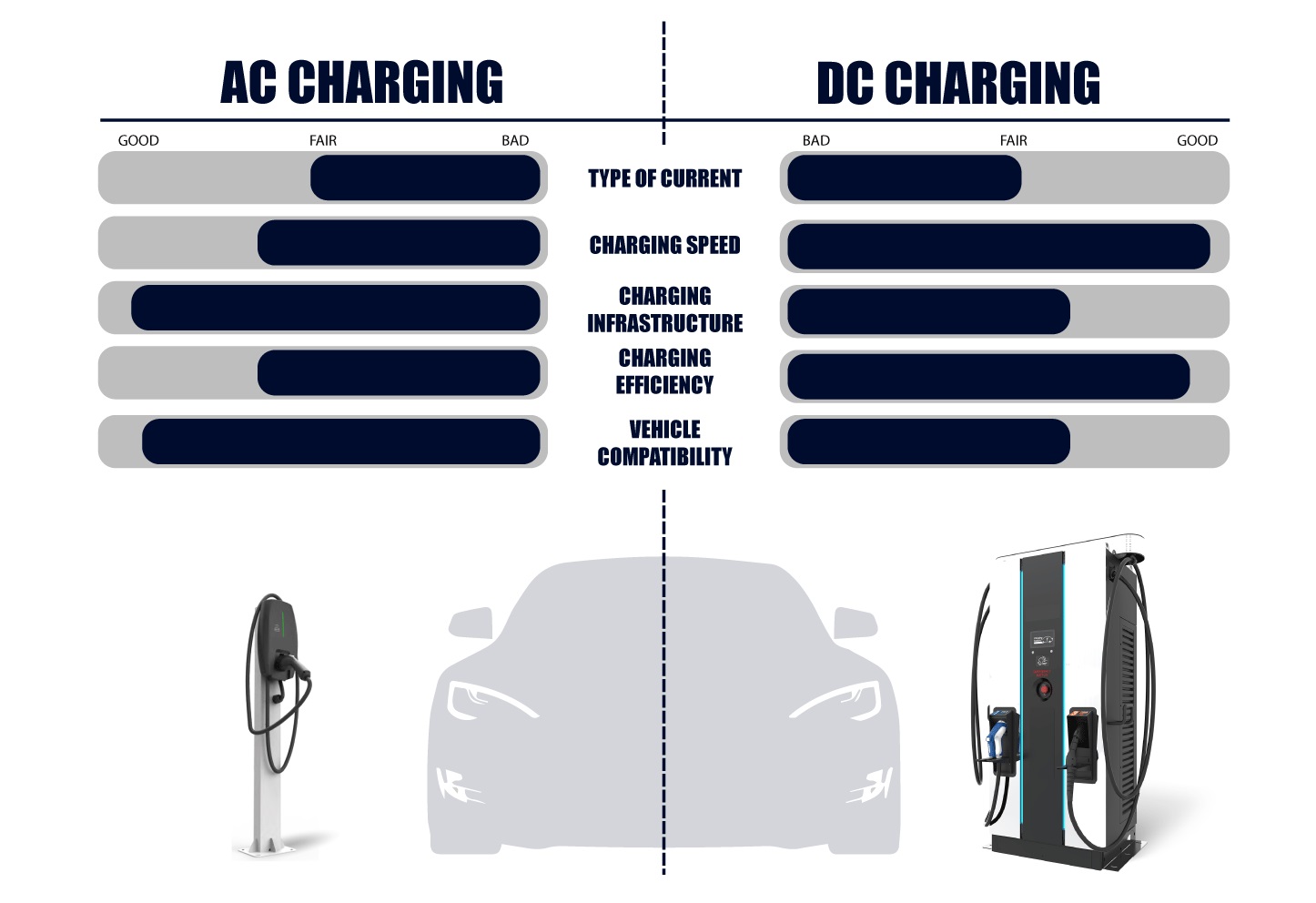
Type of Current
AC Connector: AC connectors are used for charging from standard household electrical outlets or Level 1 and Level 2 charging stations. They deliver alternating current, which is the type of electricity typically found in residential and commercial power grids.
DC Connector: DC connectors are used for fast-charging stations and deliver direct current. These connectors are capable of providing much higher charging power, making them suitable for quick charging, especially for long trips when you need a rapid recharge.
Charging Speed
AC Connector: AC charging is slower compared to DC charging. Level 1 charging (from a standard household outlet) is the slowest, while Level 2 charging (from dedicated charging stations) is faster but still not as fast as DC fast-charging.
DC Connector: DC fast-charging provides a significantly higher charging speed, allowing EVs to charge much more rapidly. This is important for long-distance travel and reducing charging time.
Charging Infrastructure
AC Connector: AC connectors are more common and widely available since they can be used with standard electrical outlets. Level 2 AC charging stations are also relatively common in public places.
DC Connector: DC fast-charging stations are less common than AC charging stations and are typically found along highways, major routes, and at specific charging network locations. They require more specialized infrastructure and equipment.
Charging Efficiency
AC Connector: AC charging is generally less efficient than DC charging, as there is an additional step in the charging process where AC must be converted to DC inside the vehicle’s onboard charger. This conversion process results in some energy loss.
DC Connector: DC charging is more efficient because it directly supplies the vehicle’s battery with the type of electricity it can use, minimizing energy loss during charging.
Vehicle Compatibility
AC Connector: All electric vehicles are equipped with onboard chargers that can accept AC power, making them compatible with AC charging infrastructure.
DC Connector: Not all electric vehicles are equipped with DC fast-charging capabilities. It depends on the vehicle’s design and whether it supports DC fast-charging standards like CCS (Combined Charging System) or CHAdeMO.
The choice between AC and DC connectors for EV charging depends on your specific needs. AC charging is more suitable for overnight or regular charging at home or work, while DC fast-charging is essential for long trips and quick top-ups when you need to get back on the road as quickly as possible. Most EVs are equipped to handle both AC and DC charging, but the availability of DC fast-charging infrastructure can vary by location.





