How does Autonomous Vehicles work?
Before exploring the differences between LiDAR and Radar, we will first explain how self-driving cars work.
Usually, highly or completely autonomous cars produce a precise long- as well as short-range map of a vehicle’s surrounds using a different sensor technology in a variety of weather and lighting situations. In order to boost redundancy and raise safety, it is crucial that the technologies intersect enough in addition to complimenting one another. The idea of sensor fusion is to combine various sensor technologies to produce a precise and trustworthy representation of the area around an AV.
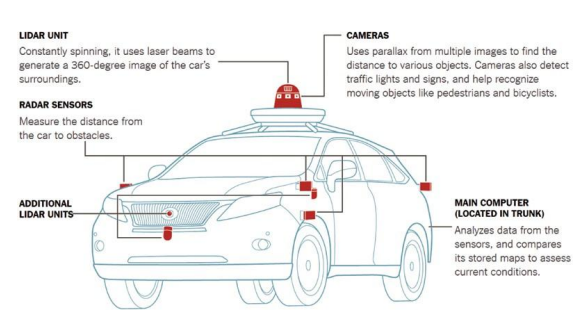
Most prototypes of self-driving cars contain LiDAR unit (constantly spinning, it uses laser beams to generate a 360-degree image of the car surrounding), camera (to detect traffic light and sign, and helps recognize moving object, radar sensor (for measuring range of nearby obstacles or vehicles), main computer (located in trunk), among other components.
Source; https://www.youtube.com/@ThomasSchwenke-knowledge
What is LiDAR?
LiDAR or Light Detection and Ranging – quite often known as laser scanners, laser radar, and sometimes Time of Flight (ToF), is a sensing technique that locates objects and calculates their distances. By shining an optical pulse on a target, the technology illuminates the object, and then it analyses the properties of the returned signal.
The optical pulse’s width might vary between a few nanoseconds and many microseconds.
LiDAR can be used for gas analysis, safety systems in manufacturing, smart munitions, including 3D aerial as well as geographic mapping. LiDAR, Ultrasonic sensing machine, Radar and cameras each have specific advantages and drawbacks.
The use of LiDAR in Autonomous Vehicles
Since the development of the laser, light detection and ranging, also known as LiDAR, has been used for a variety of purposes, including maps, surveying, military use, archaeology, farming, geology, etc.
By 2030, the market size of LiDAR might be worth $8.6 billion US dollars because to advances in LiDAR beam steering technology, ongoing cost reductions, and the development of autonomous vehicles (AV) including advanced driving assistance systems (ADAS). Automotive applications make this possible, and they can be broadly applied to other fields including robots, industry, smart towns, and mapping.
The use of Radars in Mobility
Radar or Radio Detection and Ranging is a technology where high-quality sensors are used in autonomous vehicles to ensure a reliable vision. These sensors help in detecting the obstacles or blockages if any in the vehicles driving environment and ensures that the vehicle moves without any unwanted fatalities. Besides autonomous vehicles, Radar sensors are used in a variety of fields like whether forecasting, traffic control etc.
With the advent of advanced driver assistance system or ADAS, Radar has become an integral part of modern-day cars. It has proved to be very helpful from safety point of view too. The mid, short and long-range radars are deployed in autonomous vehicles for collision mitigation (CM), line change assistance (LCA), blind spot detection (BSD), rear cross traffic alert (RCTA). Be it detecting, ranging, tracking or imaging, Radar sensors do them all with finesse.
How radar sensor works?
A Radar sensor basically is a conversion device that is used to convert microwave echo signals into electric signals. Wireless sensing technology is used to detect the object’s physical statistics as well as its motion trajectory. These sensors have unique ability to see through the walls and can detect hurdles such as glass too. They are considered to be safe for living beings as compared to other sensor technologies like ultrasound etc.
One of the major advantages of Radar sensor is its ability to detect the motion and velocity. By using any object’s Doppler Effect, these sensors can evaluate the real time speed as well the direction of the object.
Comparing LiDAR and Radar
When in comes to self-driving vehicles, what is the difference between LiDAR and radar? To answer this question we can identify and compare between various aspects like accuracy, performance, reach, cost, etc..
Accuracy
LiDAR can track details with remarkable accuracy using 3D by capturing the position, size, and shape of objects relative to the sensor.
On the other hand, Radar is a 2D technology that can capture information related to velocity and range in better accuracy compared to LiDAR, but fails to capture the full detailed surroundings meaning that some of the objects may be falsely identified or even failed to be detected.
Performance
Unlike Radar, LiDAR systems might face performance problems related to weather, like rain, fog, snow, or even direct sunlight, which may affect its accuracy. However, many manufacturers are developing LiDAR systems to resist these conditions.
Wavelength Reach
Radio wavelengths are longer than light waves, allowing Radars to transmit radio frequencies to a longer range as compared to LiDAR.
Cost
While radars are known to be more affordable and less costly to provide, this cost gap is continuously getting closer with newer LiDAR technologies.





